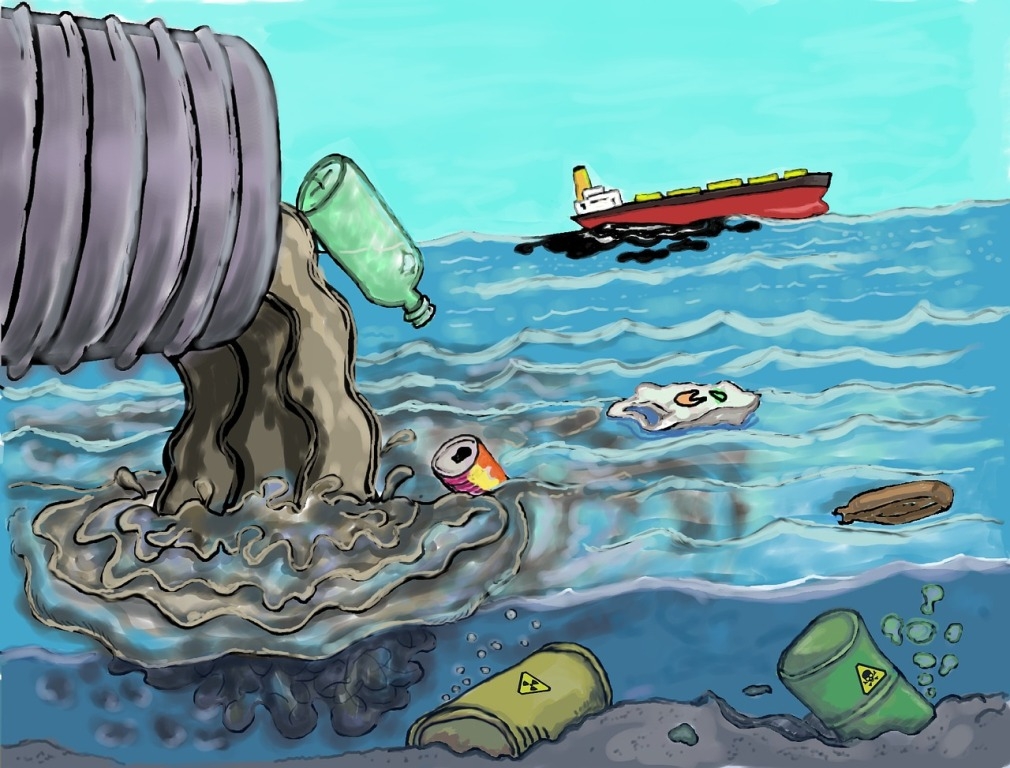
Water pollution is the contamination of water bodies usually as a result of human activities. Water bodies include lakes, rivers, oceans aquifers and ground water. Pollution results when contaminants are introduced into the natural environment. Introduction may be from releasing inadequately treated wastewater into natural water bodies which lead to degradation of aquatic ecosystems. In turn, this can lead to public health problems for people living downstream. They may use the same polluted river water for drinking or bathing or irrigation. Water pollution can be grouped into surface water pollution and ground water pollution. Sources of water pollution are either point sources or non-point sources. Point sources have one identifiable cause of pollution, such as a storm drain, wastewater treatment plant or stream. Non-point sources are more diffuse, such as agricultural runoff. Pollution is the result of cumulative effect over time. Water is typically referred to as polluted when it is impaired by anthropogenic contaminants. Due to these contaminants it either does not support a human use such as drinking water or undergoes a marked shift in its ability to support its biotic communities such as fish. Natural phenomena such as volcanos, algae blooms, storms and earthquakes also cause major changes in water quality and the ecological status of water. Water pollution is a major global problem. It requires ongoing evaluation and revision of water resources policy at all levels (International down to individual aquifers and wells).It has been suggested that water pollution is the leading worldwide cause of death and diseases. Water pollution accounted for the death of 1.8 million people in 2015. India and China are two countries with high levels of water pollution. An estimated 580 people in India die of water pollution related illness (including waterborne diseases) every day. About 90% of the water in the cities of China is polluted. As of 2007, half a billion Chinese had no access to safe drinking water. In addition to the acute problems of water pollution in developing countries, developed countries also continue to struggle with pollution problems. In a report on water quality in United States in 2009, 44% of assessed stream miles, 64% of assessed lake acres and 30% of assessed bays and estuaries square miles were classified as polluted.
Surface water pollution includes pollution of rivers, lakes and oceans. A sub set of surface water pollution is marine pollution. One common path of entry by contaminants to the sea are rivers and also directly discharging sewage and industrial waste into the ocean. Pollution such as this occurs particularly in developing nations. In fact the ten largest emitters of oceanic plastic pollution worldwide are from the most to the least ,China, Indonesia, Philippines, Vietnam, Sri Lanka, Thailand, Egypt, Malaysia, Nigeria and Bangladesh largely through the rivers Yangtze, Indus, Yellow, Hai, Niles, Ganges, Pearl, Amur, Niger and Mekong and accounting for 90% of all the plastic that reach the world’s ocean. Large gyres (vortexes) in the oceans trap floating plastic debris. Plastic debris can absorb toxic chemicals from ocean pollutions, potentially poisoning any creature that eats it. Many of these long lasting pieces end up in the stomach of marine birds and animals. This results obstruction of digestive pathways which leads to reduce appetite or even starvation. Causes of ground water pollution include: naturally occurring (geogenic), on-site sanitation system, sewage, fertilizers, and pesticides, commercial and industrial leaks, hydraulic fracturing, and landfill leachate. Surface water seeps through the soil and become ground water. Conversely, ground water can also feed surface water source. The specific contaminants leading to pollution in water include a wide spectrum of chemicals, pathogens and physical changes such as elevated temperature and discoloration. While many of the chemicals and substances that are regulated may be naturally occurring (Calcium, Sodium, Iron, manganese etc.) the concentration usually determines what is a natural contaminants. High concentration of naturally occurring substances can have negative impacts on aquatic flora and fauna. Oxygen depleting substances may be natural materials such as plant matter (e.g. leaves and grasses) as well as man-made chemicals. Other natural and anthropogenic substances may cause turbidity (cloudiness) which block light and disrupts plant growth and clogs the gills of some fish species. Pathogens or microorganisms found incontaminated surface water that have caused human health problems include:Burkholderia, Pseudo mallei, Cryptosporidium partum, Giardialamblia, Salmonella, Norovirus and other viruses ,parasitic worms including Schistosoma type. Organic water pollutants include: Detergents, disinfection by –product, food processing waste, insecticides and herbicides, petroleumhydrocarbons, volatile organic compounds, chlorinated solvents,perchlorate,various chemical compounds found in personal hygiene and cosmetic products, drug pollution involving pharmaceutical drugs and their metabolites. Inorganic water pollutants include: Sulphur dioxide from power plants, Ammonia from food processing waste, Chemical waste as industrial by-products, fertilizers containing nutrients-Nitrogen, Phosphates. Heavy metals from motor vehicle, secretion of cresol, preservative into the aquatic ecosystem, silt (sediments) in runoff from construction sites. Some of the waterborne diseases are-typhoid, cholera, paratyphoid fever, dysentery, jaundice, ameobiasis and malaria. Chemicals in water also have negative effects on our health. Pesticides- can damage the nervous system and cause cancer because of the carbonates and organophosphates that they contains. The main problem caused by water pollution is that it kills organisms that depends on these water bodies. Dead fish, crabs, birds and seagulls, dolphins and many other animals often wind up on beaches ,killed by pollutants in their habitats ( living environment).Water pollution disrupts the natural food chain as well.
Down to our tiny land log state Manipur; are our water bodies (may be rivers, lakes or public ponds) pollution free? I don’t think so. We all see thehealth condition of Nambul River which falls in Loktak Lake. Then what can we say about the quality of water in Loktak Lake? Probably Loktak could have been badly polluted as seen from the health of Nambul River.Not only Loktak Lake,lake like lamphel pat is also highly polluted by the bio-medical waste of RIMS and other Hospitals. Very recently the problem of pollution in KongbaRiver was reported due to the medical waste from JNIMS.Rejuvenation and conservation works of Nambul River began at Thong Nambonbi from 23rd May 2019 which was inaugurated by the Hon’ble Chief Minister beforeParliament Election’s Model Code of Conduct was enforced but the progress of the initiated work is yet be seen and it looks like tiger on the paper.Nambul River as such, is one of the most polluted river in the world.If we are to maintain a healthy Manipur, we need to make Loktak and our water bodies healthy which in turn need to keep NambulRiver clean and our mindset clean. That’s the only solution else we are bound to extinct which no legality in this Universe can save us.