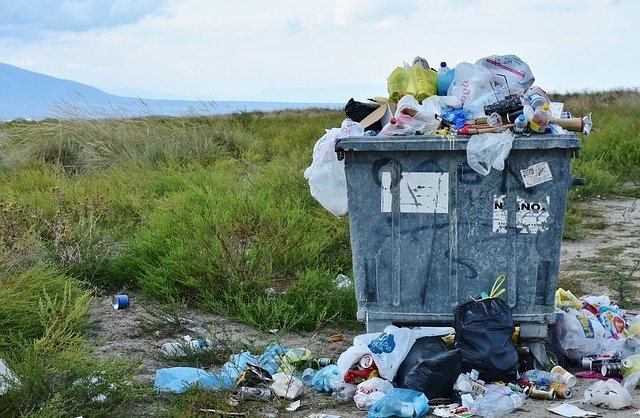
Plastic recycling is the process of recovering scrap or waste plastic and reprocessing the material into useful products. Since the vast majority of plastic is non-biodegradable, cycling is a part of global efforts to reduce the plastic in the waste stream, especially the approximately 8 million tons of waste plastic that enters the Earth’s Ocean every year. Compared with lucrative recycling of metals and similar to the low value of glass, plastic polymers recycling is often more challenging, because of low density and low value. There are also numerous technical hurdles to overcome when recycling plastic. When different types of plastics are melted together, they tend to phase separate, like oil and water and set in these layers. The phase boundaries cause structural weakness in the resulting material: meaning that polymer blends are useful in only limited applications. The two most widely manufactured plastics, polypropylene and polyethylene behave this way, which limits their utility for recycling.
Recently the use of block copolymers as “molecular stitches” or “macromolecular welding flux” has been proposed to overcome the difficulties associated with phase separation during recycling. The percentage of plastic that can be fully recycled rather than down cycled or go to waste can be increased when manufacturing of packaged goods, minimize mixing or packaging materials and eliminate contaminates. The use of biodegradable plastic or plastic which can be organically recycled or can be composted in Industrial composting is increasing for certain short lived packaging applications. Biodegradable plastics are plastics that can be decomposed by the action of living organisms, usually bacteria. Before recycling, most plastics are sorted according to their resin type. In the past, plastic re claimers used the resin identification code(RIC),a method of categorization of polymer type which was developed by the Society of Plastic Industry in 1988.Some plastic products are also separated by color before they are recycled. The plastic recyclable are then shredded. These shredded fragments then undergo processes to eliminate impurities like paper labels. The materials melted are often extruded into the form of pellets which are then used to manufacture other products. Recycling also keeps plastic out of landfills where it can take 500 years to break down.
Plastic pyrolysis can convert petroleum based waste streams such as plastic into fuels and carbons. Heat compression takes all unsorted cleaned plastic in all forms, from soft plastic bags to hard industrial waste and mixes the load in tumblers. The most obvious benefit to the method is that all plastic is recyclable, not just matching form. For some waste plastics, technical devices called recyclebots enable a form of distributed recycling. Post-consumer polyethylene terephthalate (PET or PETE) containers are sorted into different color fractions and baled for onward sale. PET recyclers further sort the baled bottles and they are washed and flaked or flaked and washed. Non-PET fractions such as caps and labels are removed during the process. The clean flake is dried. Further treatment can take place e.g melt filtering and pelletizing or various treatments to produce food-contact approved recycled PET (RPET). RPET has been widely used to produce polyester fibers. One used of this recycled PET is to create fabric to be used in clothing Industry.The recycled PET thread or yarn can be used either alone or together with other fibers to create a wide variety of fabrics. Traditionally these fabrics are used to create strong, durable, and rough products such as jackets, coats, shoes, bags, hats and accessories, since they are usually too rough for direct skin contact and can cause irritation. Other major outlets for RPET are new containers (food-contact or non-contact) produced either by molding into bottles and jars or by thermoforming APET sheet to produce clamshells, blister packs and collation trays. High density polyethylene (HDPE) is a commonly recycled plastic. HDPE’s highly crystalline structures makes it a strong high density moderately stiff plastic. Often, it is typically down cycled into plastic lumber,tables,roadside curbs,benches,trucks cargo liners,trash receptacles,stationery ( e.g rulers) and other durable plastic products and is widely in demand. Expanded polystyrene (EPS) scrap can easily be added to products such as EPS insulation sheets and other EPS materials for construction applications. When it is not used to make more EPS,foam scrap can be turned into clothes hangers, Park benches, flower pots,toys,rulers,stapler bodies,seedling containers, picture frames and architectural molding from recycled polystyrene(PS). Recycled EPS is also used in many metal casting operations.Rastra is made from EPS that is combined with cement to be used as an insulating amendment in the making of concrete foundries and walls. Since 1993 American manufacturers have produced insulating concrete forms made with approximately 80% recycled EPS. Israel have shown that plastic films recycled from mixed municipal waste streams can be recycled into useful household products such as buckets. Similarly agricultural plastics such as mulch film, drip tape and silage bags are being diverted from the recycled waste streams and successfully recycled into much larger products for Industrial applications such as plastic composite railroad ties. Historically these agricultural plastic have primarily been either land filled or burned on-site in the fields of individuals’ farms.
CNN reports that Dr.S.Madhu of Kerala Highway Research Institute,India has formulated a road surface that includes recycled plastics, aggregate ,bitumen(asphalt) with plastic that has been shredded and melted at a temperature below 2200C (4280F) to avoid pollution. This road surface is claimed to be very durable and monsoon rain resistant. Keeping in mind, lack of manufacturing opportunities in Manipur, a father –son duo from Manipur, decided to start a manufacturing unit of their own. After years of hard work, Sadokpam Itombi Singh and his father Sadokpam Gunakanta have established a successful operation of recycling program at Sagolband sadokpam leikai in Imphal. SJ Plastic Industry, started by Mr Itombi, could build pipes, other household items, tubes and flower pots from plastic waste. “Plastic is very Important and how to dispose is also equally important” Mr Itombi said. Currently as many as 120 types of plastics have been identified in Manipur alone. Out of 120, almost 30 are recycled in Manipur while the remaining are sent to Delhi and Guwahati after compression process. On 24th May 2018, Chairman Manipur Pollution Control Board also sent a written intimation to the Manipur Public Works Dept. giving instruction to make use of plastic waste in road construction mandatory in the state as is done in Kerala. It will be a good step forward if Government of Manipur execute this practice in reality to avoid the threat of plastic pollution in our Environment. Plastic are recyclable, we need to make conscious efforts to recycle such waste so that they can be used for other purpose, instead of allowing them to pollute our water bodies and land.